

So, the ray XA is launched from denser medium to rarer medium by making an angle α with the fiber axis.

The figure below shows an optical fiber inside which light ray is focused. The refractive index of the core is ƞ 1 and that of cladding is ƞ 2. Derivation for Numerical Aperture of Optical FiberĬonsider a light ray XA, that incident inside the optical fiber. So, let us now understand the numerical aperture for optical fiber in detail. So, the light is propagated inside the fiber by performing continuous reflections from the cladding.īut the condition of total internal reflection for the propagation of light ray comes into action only when most of the light is collected inside the fiber. Propagation through Optical fiberĪs we have already discussed that light through an optical fiber is propagated by several continuous total internal reflections.Īs we know that an optical fiber is composed of a core which is made up of a very pure form of glass silica and is surrounded by a glass cladding. Hence the acceptance angle and numerical aperture are related to each other. As acceptance angle is that max angle through which light enters the fiber.
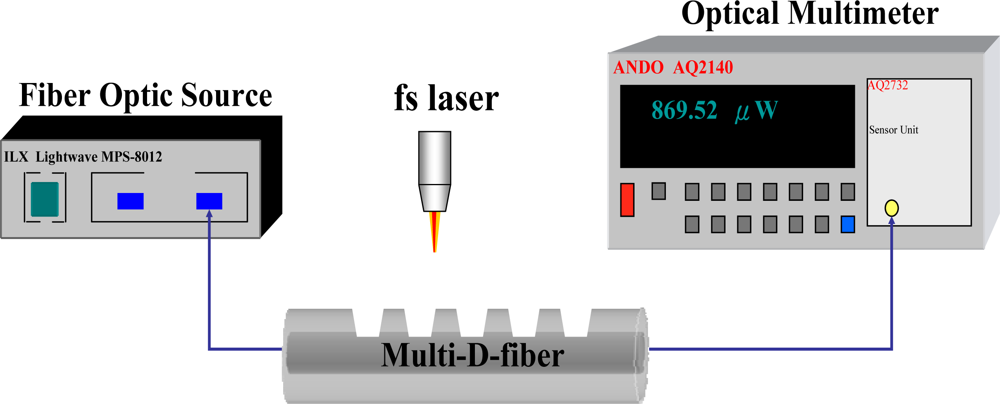
Thus we can say that the light gathering efficiency of an optical fiber is the key characteristic while transmitting a signal through an optical fiber. Or we can say multiple TIR takes place inside the optical fiber for the light ray to get transmitted from an end to another through an optical fiber.īasically when the light is emitted from an optical source, then the fiber must be highly efficient so as to collect the maximal emitted radiation inside it. We know light through an optical fiber is propagated through total internal reflection. Numerical aperture is abbreviated as NA and shows the efficiency with which light is collected inside the fiber in order to get propagated.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
